
Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1979. The Hydrogen Spectrum In the spectrum, we can see sets or families of lines Balmer could not explain why the lines were formed - an explanation had to wait. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1963. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press, 1996. Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin: An Autobiography and Other Recollections. This lecture gives more details about the atomic spectra of hydrogen along with matter/energy interactions involving atomic hydrogen. Lecture Slides (PDF - 1.3MB) Lecture Summary Line spectra the Bohr model uses of emission and absorption spectra 6.3, “Atomic Spectra and Models of the Atom.” Describe the ground state of the gas phase atom.Īrchived Lecture Notes #1 (PDF), Sections 3, 5 This page introduces the atomic hydrogen emission spectrum, showing how it arises from electron movements between energy levels within the atom. So, if a nucleus has Z Z protons (Z 1 Z 1 for hydrogen, 2 for helium, etc.) and only one electron, that atom is called a hydrogen-like atom.Explain trends in ionization energy across the periodic table. For the hydrogen atom,, , and, where is the elementary charge, is the vacuum permittivity, is the Bohr radius, is the principal quantum number, is the azimuthal quantum number and is the distance of the electron from the nucleus.Calculate the energy of an electron in the ground state of hydrogen.Explain why the radius of the electron orbital takes multiple values that are discrete, quantized, and non-linear.Describe how the atomic spectra of hydrogen is produced.
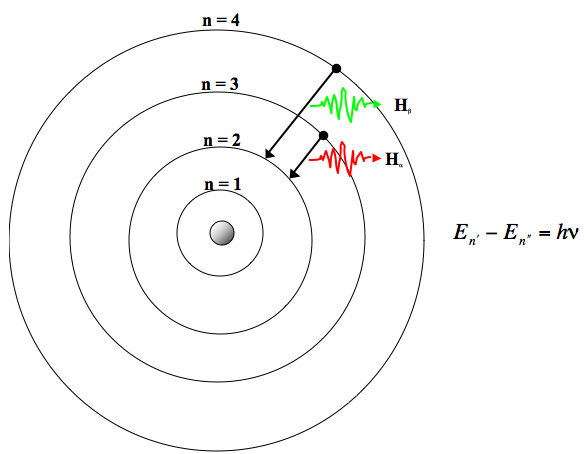
Learning ObjectivesĪfter completing this session, you should be able to: Sadoway discusses the shell model and quantum numbers ( Session 5). Session 3: Atomic Models: Rutherford & Bohr.Matter/Energy Interactions: Atomic SpectraĪtomic spectra of hydrogen, matter/energy interactions involving atomic hydrogen, planetary model, Bohr’s postulates, quantum condition, ionization energy, electron orbital transitionsĪngstrom, Avogadro’s number, prism, refraction, wavelength, nanometer, Johann Balmer, wavenumber, Michael Faraday, cathode, anode, electron-volt, Bohr radius, ground state, ionization energy, energy level, conservation of energy, atomic spectra, Cecilia Payne, Ernest Rutherford, joule, coulomb, Max Planck, Planck’s constant, emission spectra, spectrograph, electrode, photon, volt, radiationĬhemical analysis, analyzing composition of stars, televisionīefore starting this session, you should be familiar with:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
